The CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machine tool industry relies heavily on precision, power, and reliability. At the heart of many CNC machines lies the gear motor, a vital component responsible for translating rotational motion from an electric motor into controlled, precise movement. Understanding the principles behind gear motor manufacturing and comparing their performance characteristics is crucial for optimizing CNC machine tool performance and achieving higher levels of automation and efficiency. This article delves into the core aspects of gear motors used in CNC applications, examining different manufacturing methods, key performance indicators, and a comparison of popular types.
I. Principles of Gear Motor Manufacturing
Gear motors, as the name suggests, combine an electric motor with a gear train. The electric motor provides the rotational power, while the gear train is responsible for reducing the motor's speed and increasing its torque. This combination is what allows for the controlled and powerful movements required by CNC machines. There are several primary manufacturing methods used to create gear motors, each with its own advantages and disadvantages:
Spur Gears: These are the simplest and most common type of gear. They have straight teeth that are parallel to the axis of rotation. They are inexpensive to manufacture but can be noisy, especially at higher speeds. They are often used in applications where cost is a major concern and precise positioning isn't paramount.
Helical Gears: Helical gears have teeth that are angled along the axis of rotation. This offers smoother and quieter operation compared to spur gears, as the teeth engage gradually. They also transmit more power and can handle higher loads. However, they are more expensive to manufacture.
Bevel Gears: These gears have teeth cut on a sloping surface. They are used to transmit power between shafts that are at an angle to each other. They’re commonly found in gearboxes that manage complex motion paths in CNC machines.
Worm Gears: Worm gears use a worm (a screw-like gear) to drive a worm wheel (a gear with angled teeth). This allows for a high gear ratio in a compact space. Worm gears can operate silently and provide self-locking capabilities, meaning they can hold a position without requiring external braking. However, they are generally less efficient than other gear types.
The material used in gear motor construction is also a critical factor. Common materials include steel (for high strength and durability), aluminum (for lighter weight), and plastics (for cost-effectiveness and low noise). The choice of material depends on the application requirements, including the required torque, speed, and operating environment.
II. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Several KPIs are essential for evaluating the performance of a gear motor in a CNC application. These include:
Gear Ratio: This is the ratio of the input speed (motor speed) to the output speed (gear motor speed). A higher gear ratio results in lower output speed and higher torque. CNC machines often require precise control over the output speed, making the gear ratio a critical factor.
Torque: This is the rotational force produced by the gear motor. Higher torque allows the machine to perform heavier cutting operations and handle higher loads. CNC machines routinely require high torque for operations like milling and drilling.
Efficiency: This is the ratio of output power to input power. Higher efficiency means less energy is wasted as heat, leading to lower operating costs and reduced heat generation within the machine tool.
Resolution/Accuracy: Crucial for CNC machines, resolution refers to the smallest increment of movement the gear motor can achieve. This directly impacts the accuracy of the final product. Specialized gear designs and high-precision manufacturing are necessary to achieve high resolution.
Noise Level: Excessive noise can be disruptive and indicate inefficiencies or mechanical issues. Careful gear design and material selection can minimize noise generation.
Duty Cycle: This refers to the percentage of time the gear motor can operate continuously without overheating or failure. CNC machines often operate for extended periods, so a high duty cycle is essential.
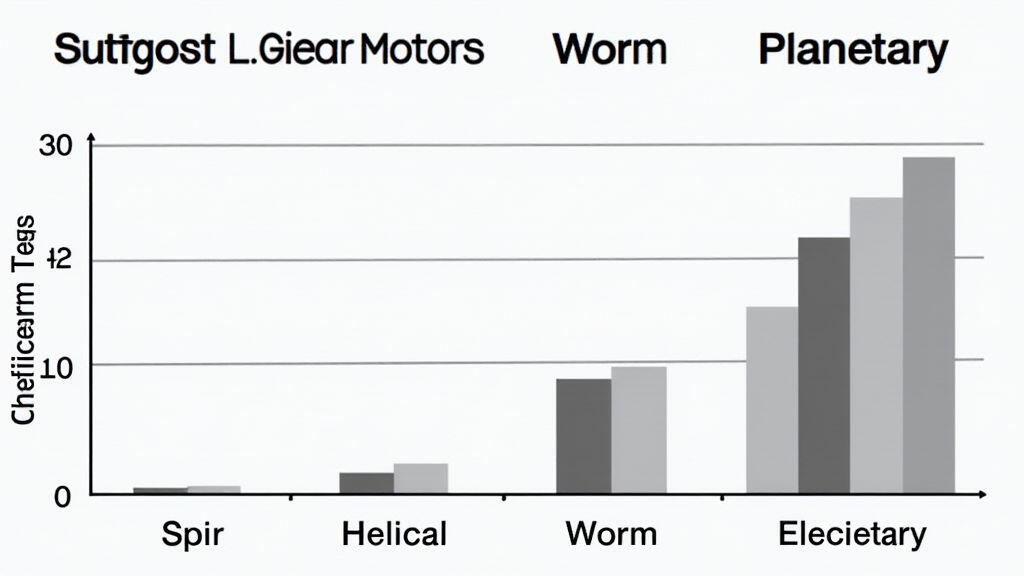
III. Performance Comparison of Gear Motor Types in CNC Applications
Choosing the right type of gear motor is critical for optimizing CNC machine tool performance. Here’s a brief comparison of the most common types:
Spur Gear Motors: Suitable for less demanding applications like spindle rotation in smaller CNC machines or auxiliary functions. They offer cost-effectiveness but may lack the precision and quiet operation required for high-precision machining.
Helical Gear Motors: A popular choice for a wide range of CNC applications, offering a good balance of torque, speed, and noise reduction. They’re often used in linear motion stages and rotary tables. Their smoother operation contributes to improved machining accuracy and reduces vibration.
Worm Gear Motors: Well-suited for applications requiring high gear ratios and self-locking capabilities, such as positioning systems where maintaining a specific position is crucial. They're employed in axes requiring precise homing and holding positions. However, their lower efficiency needs to be considered.
Planetary Gear Motors: These offer high torque density (high torque for their size and weight) and high efficiency. They are becoming increasingly popular in high-end CNC machines where space and power efficiency are important. They are often utilized in high-speed spindles and complex motion systems.
IV. Trending Events and Future Potential
The CNC machine tool industry is continually evolving, driven by trends like Industry 4.0, automation, and the increasing demand for precision and flexibility. The demand for faster, more accurate, and more energy-efficient CNC machines is fueling innovation in gear motor technology.
Specifically, the rise of 5-axis machining and complex tooling demands higher torque density and improved precision from gear motors. The integration of IoT (Internet of Things) sensors into gear motors allows for real-time monitoring of performance and predictive maintenance, minimizing downtime. Furthermore, research into advanced materials and gear designs promises to enhance efficiency, reduce noise, and extend the lifespan of gear motors. Planetary gear motors are poised for significant growth as they address the needs of high-performance applications.
V. Conclusion
Gear motors are fundamental components of CNC machine tools, playing a crucial role in achieving precise and efficient manufacturing processes. Understanding the principles of their manufacturing, the importance of key performance indicators, and the strengths and weaknesses of different gear types allows engineers to select the optimal motor for a given application. As the CNC industry continues to advance, driven by trends like Industry 4.0 and more complex machining operations, the development of higher-performance, more efficient, and more intelligent gear motors will remain a critical area of innovation. The integration of advanced materials, improved gear designs, and IoT technologies will further enhance the capabilities of CNC machines, pushing the boundaries of precision manufacturing and solidifying the crucial role of gear motors within this dynamic industry.
Leave A Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fiels are marked